Swine flu
From DrugPedia: A Wikipedia for Drug discovery
Swine influenza (also called H1N1 flu, swine flu, hog flu, and pig flu) is an infection by any one of several types of swine influenza virus. Swine influenza virus (SIV) is any strain of the influenza family of viruses that is endemic in pigs.<ref name=Merck> "Swine influenza" (2008). The Merck Veterinary Manual. Retrieved on April 30, 2009.</cite></ref> As of 2009, the known SIV strains include influenza C and the subtypes of influenza A known as H1N1, H1N2, H3N1, H3N2, and H2N3.
Swine influenza virus is common throughout pig populations worldwide. Transmission of the virus from pigs to humans is not common and does not always lead to human influenza, often resulting only in the production of antibodies in the blood. If transmission does cause human influenza, it is called zoonotic swine flu. People with regular exposure to pigs are at increased risk of swine flu infection. The meat of an infected animal poses no risk of infection when properly cooked.
During the mid-20th century, identification of influenza subtypes became possible, allowing accurate diagnosis of transmission to humans. Since then, only 50 such transmissions have been confirmed. These strains of swine flu rarely pass from human to human. Symptoms of zoonotic swine flu in humans are similar to those of influenza and of influenza-like illness in general, namely chills, fever, sore throat, muscle pains, severe headache, coughing, weakness and general discomfort.
Contents |
[edit] Classification
Of the three genera of influenza viruses that cause human flu, two also cause influenza in pigs, with influenza A being common in pigs and influenza C being rare.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Heinen PP (15 September 2003). "Swine influenza: a zoonosis". Veterinary Sciences Tomorrow. ISSN 1569-0830. “Influenza B and C viruses are almost exclusively isolated from man, although influenza C virus has also been isolated from pigs and influenza B has recently been isolated from seals.”</cite></ref> Influenza B has not been reported in pigs. Within influenza A and influenza C, the strains found in pigs and humans are largely distinct, although due to reassortment there have been transfers of genes among strains crossing swine, avian, and human species boundaries.
[edit] Influenza C
Influenza C viruses infect both humans and pigs, but do not infect birds.<ref name=Bouvier><cite style="font-style:normal">Bouvier NM, Palese P (September 2008). "The biology of influenza viruses". Vaccine 26 Suppl 4: D49–53. PMID 19230160.</cite></ref> Transmission between pigs and humans have occurred in the past.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Kimura H, Abiko C, Peng G, et al (April 1997). "Interspecies transmission of influenza C virus between humans and pigs". Virus Res. 48 (1): 71–9. PMID 9140195.</cite></ref> For example, influenza C caused small outbreaks of a mild form of influenza amongst children in Japan<ref name=Matsuzaki><cite style="font-style:normal">Matsuzaki Y, Sugawara K, Mizuta K, et al (February 2002). "Antigenic and genetic characterization of influenza C viruses which caused two outbreaks in Yamagata City, Japan, in 1996 and 1998". J. Clin. Microbiol. 40 (2): 422–9. PMID 11825952. PMC:153379.</cite></ref> and California.<ref name=Matsuzaki/> Due to its limited host range and the lack of genetic diversity in influenza C, this form of influenza does not cause pandemics in humans.<ref name=Lynch><cite style="font-style:normal">Lynch JP, Walsh EE (April 2007). "Influenza: evolving strategies in treatment and prevention". Semin Respir Crit Care Med 28 (2): 144–58. doi:. PMID 17458769.</cite></ref>
[edit] Influenza A
Swine influenza is known to be caused by influenza A subtypes H1N1,<ref name = Iowa/> H1N2,<ref name = Iowa> Template:Cite web</ref> H3N1,<ref> <cite style="font-style:normal">Shin JY, Song MS, Lee EH, Lee YM, Kim SY, Kim HK, Choi JK, Kim CJ, Webby RJ, Choi YK (2006). "Isolation and characterization of novel H3N1 swine influenza viruses from pigs with respiratory diseases in Korea". Journal of Clinical Microbiology 44 (11): 3923–7. doi:. PMID 16928961.</cite></ref> H3N2,<ref name = Iowa/> and H2N3.<ref> <cite style="font-style:normal">Ma W, Vincent AL, Gramer MR, Brockwell CB, Lager KM, Janke BH, Gauger PC, Patnayak DP, Webby RJ, Richt JA (26 December 2007). "Identification of H2N3 influenza A viruses from swine in the United States". Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104 (52): 20949–54. doi:. PMID 18093945. PMC:2409247.</cite></ref> In pigs, three influenza A virus subtypes (H1N1, H3N2, and H1N2) are the most common strains worldwide.<ref name=Kothalawala/> In the United States, the H1N1 subtype was exclusively prevalent among swine populations before 1998; however, since late August 1998, H3N2 subtypes have been isolated from pigs. As of 2004, H3N2 virus isolates in US swine and turkey stocks were triple reassortants, containing genes from human (HA, NA, and PB1), swine (NS, NP, and M), and avian (PB2 and PA) lineages.<ref> <cite style="font-style:normal">Yassine HM, Al-Natour MQ, Lee CW, Saif YM (November 2007). "Interspecies and intraspecies transmission of triple reassortant H3N2 influenza A viruses". Virol J 28 (4). doi:. PMID 18045494.</cite></ref>
[edit] Surveillance
thumb|right|Thermal scanning of passengers arriving at Singapore Changi airport. Template:Expand Although there is no formal national surveillance system in the United States to determine what viruses are circulating in pigs,<ref name="MMWR5815a5"> Template:Cite web</ref> there is an informal surveillance network in the United States that is part of a world surveillance network.
Veterinary medical pathologist, Tracey McNamara, set up a national disease surveillance system in zoos because the zoos do active disease surveillance and many of the exotic animals housed there have broad susceptibilities. Many species fall below the radar of any federal agencies (including dogs, cats, pet prairie dogs, zoo animals, and urban wildlife), even though they may be important in the early detection of human disease outbreaks.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> <ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
[edit] History
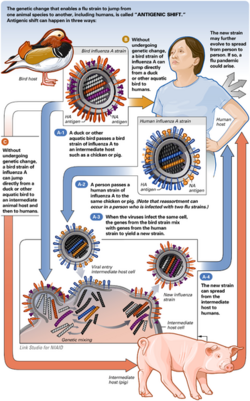
Swine influenza was first proposed to be a disease related to human influenza during the 1918 flu pandemic, when pigs became sick at the same time as humans.<ref name=Knobler>Template:Cite book</ref> The first identification of an influenza virus as a cause of disease in pigs occurred about ten years later, in 1930.<ref name="pmid12034486" /> For the following 60 years, swine influenza strains were almost exclusively H1N1. Then, between 1997 and 2002, new strains of three different subtypes and five different genotypes emerged as causes of influenza among pigs in North America. In 1997-1998, H3N2 strains emerged. These strains, which include genes derived by reassortment from human, swine and avian viruses, have become a major cause of swine influenza in North America. Reassortment between H1N1 and H3N2 produced H1N2. In 1999 in Canada, a strain of H4N6 crossed the species barrier from birds to pigs, but was contained on a single farm.<ref name="pmid12034486"><cite style="font-style:normal">Olsen CW (May 2002). "The emergence of novel swine influenza viruses in North America". Virus Research 85 (2): 199–210. PMID 12034486.</cite></ref>
The H1N1 form of swine flu is one of the descendants of the strain that caused the 1918 flu pandemic.<ref name=NYT76>Template:Cite news</ref><ref name=Pandemic/> As well as persisting in pigs, the descendants of the 1918 virus have also circulated in humans through the 20th century, contributing to the normal seasonal epidemics of influenza.<ref name=Pandemic/> However, direct transmission from pigs to humans is rare, with only 12 cases in the U.S. since 2005.<ref>Template:Cite news</ref> Nevertheless, the retention of influenza strains in pigs after these strains have disappeared from the human population might make pigs a reservoir where influenza viruses could persist, later emerging to reinfect humans once human immunity to these strains has waned.<ref name=Heinen2003>Template:Citation</ref>
Swine flu has been reported numerous times as a zoonosis in humans, usually with limited distribution, rarely with a widespread distribution. Outbreaks in swine are common and cause significant economic losses in industry, primarily by causing stunting and extended time to market. For example, this disease costs the British meat industry about £65 million every year.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Kay RM, Done SH, Paton DJ (August 1994). "Effect of sequential porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome and swine influenza on the growth and performance of finishing pigs". Vet. Rec. 135 (9): 199–204. PMID 7998380.</cite></ref>
[edit] 1918 pandemic in humans
The 1918 flu pandemic in humans was associated with H1N1 and influenza appearing in pigs;<ref name=Pandemic> <cite style="font-style:normal">Taubenberger JK, Morens DM (2006). "1918 Influenza: the mother of all pandemics". Emerg Infect Dis 12 (1): 15–22. PMID 16494711.</cite></ref> this may reflect a zoonosis either from swine to humans, or from humans to swine. Although it is not certain in which direction the virus was transferred, some evidence suggests that, in this case, pigs caught the disease from humans.<ref name=Knobler/> For instance, swine influenza was only noted as a new disease of pigs in 1918, after the first large outbreaks of influenza amongst people.<ref name=Knobler/> Although a recent phylogenetic analysis of more recent strains of influenza in humans, birds, and swine suggests that the 1918 outbreak in humans followed a reassortment event within a mammal,<ref name="pmid18353690"><cite style="font-style:normal">Vana G, Westover KM (June 2008). "Origin of the 1918 Spanish influenza virus: a comparative genomic analysis". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 47 (3): 1100–10. doi:. PMID 18353690.</cite></ref> the exact origin of the 1918 strain remains elusive.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Antonovics J, Hood ME, Baker CH (April 2006). "Molecular virology: was the 1918 flu avian in origin?". Nature 440 (7088): E9; discussion E9–10. doi:. PMID 16641950.</cite></ref> It is estimated that anywhere from 50 to 100 million people were killed worldwide.<ref name=Pandemic/><ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Patterson, KD; Pyle GF (Spring 1991). "The geography and mortality of the 1918 influenza pandemic". Bull Hist Med. 65 (1): 4–21. PMID 2021692.</cite></ref>
[edit] 1976 U.S. outbreak
On February 5, 1976, in the United States an army recruit at Fort Dix said he felt tired and weak. He died the next day and four of his fellow soldiers were later hospitalized. Two weeks after his death, health officials announced that the cause of death was a new strain of swine flu. The strain, a variant of H1N1, is known as A/New Jersey/1976 (H1N1). It was detected only from January 19 to February 9 and did not spread beyond Fort Dix.<ref name="Gaydos+2006"><cite style="font-style:normal">Gaydos JC, Top FH, Hodder RA, Russell PK (January 2006). "Swine influenza a outbreak, Fort Dix, New Jersey, 1976". Emerging Infectious Diseases 12 (1): 23–8. PMID 16494712.</cite></ref>
This new strain appeared to be closely related to the strain involved in the 1918 flu pandemic. Moreover, the ensuing increased surveillance uncovered another strain in circulation in the U.S.: A/Victoria/75 (H3N2) spread simultaneously, also caused illness, and persisted until March.<ref name="Gaydos+2006"/> Alarmed public-health officials decided action must be taken to head off another major pandemic, and urged President Gerald Ford that every person in the U.S. be vaccinated for the disease.<ref>Template:Cite news</ref>
The vaccination program was plagued by delays and public relations problems.<ref>Richard E. Neustadt and Harvey V. Fineberg. (1978). The Swine Flu Affair: Decision-Making on a Slippery Disease. National Academies Press.</ref> On October 1, 1976, the immunization program began and by October 11, approximately 40 million people, or about 24% of the population, had received swine flu immunizations. That same day, three senior citizens died soon after receiving their swine flu shots and there was a media outcry linking the deaths to the immunizations, despite the lack of positive proof. According to science writer Patrick Di Justo, however, by the time the truth was known — that the deaths were not proven to be related to the vaccine — it was too late. "The government had long feared mass panic about swine flu — now they feared mass panic about the swine flu vaccinations." This became a strong setback to the program.<ref name=DiJusto>"The Last Great Swine Flu Epidemic", Salon.com, April 28, 2009.</ref>
There were reports of Guillain-Barré syndrome, a paralyzing neuromuscular disorder, affecting some people who had received swine flu immunizations. This syndrome is a rare side-effect of modern influenza vaccines, with an incidence of about one case per million vaccinations.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Vellozzi C, Burwen DR, Dobardzic A, Ball R, Walton K, Haber P (March 2009). "Safety of trivalent inactivated influenza vaccines in adults: Background for pandemic influenza vaccine safety monitoring". Vaccine 27 (15): 2114–2120. doi:. PMID 19356614.</cite></ref> As a result, Di Justo writes that "the public refused to trust a government-operated health program that killed old people and crippled young people." In total, less than 33% of the population had been immunized by the end of 1976. The National Influenza Immunization Program was effectively halted on December 16.
Overall, there were about 500 cases of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), resulting in death from severe pulmonary complications for 25 people, which, according to Dr. P. Haber, were probably caused by an immunopathological reaction to the 1976 vaccine. Other influenza vaccines have not been linked to GBS, though caution is advised for certain individuals, particularly those with a history of GBS.<ref> <cite style="font-style:normal">Haber P, Sejvar J, Mikaeloff Y, Destefano F (2009). "Vaccines and Guillain-Barré syndrome". Drug Saf 32 (4): 309–23. doi:10.2165/00002018-200932040-00005 (inactive 2009-04-26). PMID 19388722.</cite></ref><ref> Template:Cite web</ref> Still, as observed by a participant in the immunization program, the vaccine killed more Americans than the disease did.<ref>BBC: The World; April 28, 2009.</ref>
[edit] 1988 zoonosis
In September 1988, a swine flu virus killed one woman and infected others. 32-year old Barbara Ann Wieners was eight months pregnant when she and her husband, Ed, became ill after visiting the hog barn at a county fair in Walworth County, Wisconsin. Barbara died eight days later, after developing pneumonia.<ref name="pmid2153372"><cite style="font-style:normal">McKinney WP, Volkert P, Kaufman J (January 1990). "Fatal swine influenza pneumonia during late pregnancy". Archives of Internal Medicine 150 (1): 213–5. PMID 2153372.</cite></ref> The only pathogen identified was an H1N1 strain of swine influenza virus.<ref name="pmid9511782"><cite style="font-style:normal">Kimura K, Adlakha A, Simon PM (March 1998). "Fatal case of swine influenza virus in an immunocompetent host". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. Mayo Clinic 73 (3): 243–5. PMID 9511782.</cite></ref> Doctors were able to induce labor and deliver a healthy daughter before she died. Her husband recovered from his symptoms.
Influenza-like illness (ILI) was reportedly widespread among the pigs exhibited at the fair. 76% of 25 swine exhibitors aged 9 to 19 tested positive for antibody to SIV, but no serious illnesses were detected among this group. Additional studies suggested between one and three health care personnel who had contact with the patient developed mild influenza-like illnesses with antibody evidence of swine flu infection. However, there was no community outbreak.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref><ref name="pmid1845913"><cite style="font-style:normal">Wells DL, Hopfensperger DJ, Arden NH, Harmon MW, Davis JP, Tipple MA, Schonberger LB (1991). "Swine influenza virus infections. Transmission from ill pigs to humans at a Wisconsin agricultural fair and subsequent probable person-to-person transmission". JAMA : the Journal of the American Medical Association 265 (4): 478–81. PMID 1845913.</cite></ref>
[edit] 1998 US outbreak in swine
In 1998, swine flu was found in pigs in four U.S. states. Within a year, it had spread through pig populations across the United States. Scientists found that this virus had originated in pigs as a recombinant form of flu strains from birds and humans. This outbreak confirmed that pigs can serve as a crucible where novel influenza viruses emerge as a result of the reassortment of genes from different strains.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Stephanie Desmon (April 28, 2009). "Expert: Swine flu virus more complex than typically seen". Baltimore Sun.</cite></ref><ref>Template:Cite web</ref><ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
[edit] 2007 Philippine outbreak in swine
Template:Expand On August 20, 2007 Department of Agriculture officers investigated the outbreak (epizootic) of swine flu in Nueva Ecija and Central Luzon, Philippines. The mortality rate is less than 10% for swine flu, unless there are complications like hog cholera. On July 27, 2007, the Philippine National Meat Inspection Service (NMIS) raised a hog cholera "red alert" warning over Metro Manila and 5 regions of Luzon after the disease spread to backyard pig farms in Bulacan and Pampanga, even if these tested negative for the swine flu virus.<ref> Template:Cite news</ref><ref> Template:Cite news</ref>
[edit] 2009 outbreak in humans
The H1N1 viral strain implicated in the 2009 flu pandemic among humans often is called "swine flu" because initial testing showed many of the genes in the virus were similar to influenza viruses normally occurring in North American swine.<ref name="NewSci-20090424-pandemic">Template:Cite news</ref> But further research has shown that the outbreak is due to a new strain of H1N1 not previously reported in pigs.
In late April, Margaret Chan, the World Health Organization's director-general, declared a "public health emergency of international concern" under the rules of the WHO's new International Health Regulations when the first cases of the H1N1 virus were reported in the United States.<ref name="CDCdispatch"><cite style="font-style:normal"> "Outbreak of Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection --- Mexico, March--April 2009" (30 April 2009). Centers for Disease Control.</cite></ref> <ref name="KahnHysteria"><cite style="font-style:normal">Laura H. Kahn (11 May 2009). "Stirring up "swine flu" hysteria". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists.</cite></ref> Following the outbreak, on May 2, 2009, it was reported in pigs at a farm in Alberta, Canada, with a link to the outbreak in Mexico. The pigs are suspected to have caught this new strain of virus from a farm worker who recently returned from Mexico, then showed symptoms of an influenza-like illness.<ref>Template:Cite news</ref> These are probable cases, pending confirmation by laboratory testing.
The new strain was initially described as an apparent reassortment of at least four strains of influenza A virus subtype H1N1, including one strain endemic in humans, one endemic in birds, and two endemic in swine.<ref name="NewSci-20090424-pandemic">Template:Cite news</ref> Subsequent analysis suggested it was a reassortment of just two strains, both found in swine.<ref name="Trifonov+2009"><cite style="font-style:normal">V Trifonov, H Khiabanian, B Greenbaum, R Rabadan (30 April 2009). "The origin of the recent swine influenza A(H1N1) virus infecting humans". Eurosurveillance 4 (17).</cite></ref> Although initial reports identified the new strain as swine influenza (i.e., a zoonosis originating in swine), its origin is unknown. Several countries took precautionary measures to reduce the chances for a global pandemic of the disease.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> The Swine flu has been compared to other similar types of influenza virus in terms of mortality: "in the US it appears that for every 1000 people who get infected, about 40 people need admission to hospital and about one person dies".<ref>ref name="Crikey - Take a deep breath, Swine Flu’s not that bad">Template:Cite news</ref>. There are fears that swine flu will become a major global pandemic in the winter months, with many countries planning major vaccination campaigns. <ref>"http://www.reuters.com/article/europeCrisis/idUSN09437556" Reuters Report</ref>
[edit] Transmission
[edit] Transmission between pigs
Influenza is quite common in pigs, with about half of breeding pigs having been exposed to the virus in the US.<ref name=cfsph/> Antibodies to the virus are also common in pigs in other countries.<ref name=cfsph/>
The main route of transmission is through direct contact between infected and uninfected animals.<ref name=Kothalawala/> These close contacts are particularly common during animal transport. Intensive farming may also increase the risk of transmission, as the pigs are raised in very close proximity to each other.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Gilchrist MJ, Greko C, Wallinga DB, Beran GW, Riley DG, Thorne PS (February 2007). "The potential role of concentrated animal feeding operations in infectious disease epidemics and antibiotic resistance". Environ. Health Perspect. 115 (2): 313–6. doi:. PMID 17384785.</cite></ref><ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Saenz RA, Hethcote HW, Gray GC (2006). "Confined animal feeding operations as amplifiers of influenza". Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 6 (4): 338–46. doi:. PMID 17187567.</cite></ref> The direct transfer of the virus probably occurs either by pigs touching noses, or through dried mucus. Airborne transmission through the aerosols produced by pigs coughing or sneezing are also an important means of infection.<ref name=Kothalawala/> The virus usually spreads quickly through a herd, infecting all the pigs within just a few days.<ref name=Merck/> Transmission may also occur through wild animals, such as wild boar, which can spread the disease between farms.<ref>Template:Citation</ref>
[edit] Transmission to humans
People who work with poultry and swine, especially people with intense exposures, are at increased risk of zoonotic infection with influenza virus endemic in these animals, and constitute a population of human hosts in which zoonosis and reassortment can co-occur.<ref name="pmid19276439"><cite style="font-style:normal">Gray GC, Kayali G (April 2009). "Facing pandemic influenza threats: the importance of including poultry and swine workers in preparedness plans". Poultry Science 88 (4): 880–4. doi:. PMID 19276439.</cite></ref> Vaccination of these workers against influenza and surveillance for new influenza strains among this population may therefore be an important public health measure.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Gray GC, Trampel DW, Roth JA (May 2007). "Pandemic influenza planning: shouldn't swine and poultry workers be included?". Vaccine 25 (22): 4376–81. doi:. PMID 17459539.</cite></ref> Transmission of influenza from swine to humans who work with swine was documented in a small surveillance study performed in 2004 at the University of Iowa.<ref name="pmid18258038"><cite style="font-style:normal">Gray GC, McCarthy T, Capuano AW, Setterquist SF, Olsen CW, Alavanja MC (December 2007). "Swine workers and swine influenza virus infections". Emerging Infectious Diseases 13 (12): 1871–8. PMID 18258038.</cite></ref> This study among others forms the basis of a recommendation that people whose jobs involve handling poultry and swine be the focus of increased public health surveillance.<ref name="pmid19276439"/> Other professions at particular risk of infection are veterinarians and meat processing workers, although the risk of infection for both of these groups is lower than that of farm workers.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Myers KP, Olsen CW, Setterquist SF, et al (January 2006). "Are swine workers in the United States at increased risk of infection with zoonotic influenza virus?". Clin. Infect. Dis. 42 (1): 14–20. doi:. PMID 16323086.</cite></ref>
[edit] Interaction with avian H5N1 in pigs
Pigs are unusual as they can be infected with influenza strains that usually infect three different species: pigs, birds and humans.<ref name=Thacker><cite style="font-style:normal">Thacker E, Janke B (February 2008). "Swine influenza virus: zoonotic potential and vaccination strategies for the control of avian and swine influenzas". J. Infect. Dis. 197 Suppl 1: S19–24. doi:. PMID 18269323.</cite></ref> This makes pigs a host where influenza viruses might exchange genes, producing new and dangerous strains.<ref name=Thacker/> Avian influenza virus H3N2 is endemic in pigs in China and has been detected in pigs in Vietnam, increasing fears of the emergence of new variant strains.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Yu, H. (March 2008). "Genetic evolution of swine influenza A (H3N2) viruses in China from 1970 to 2006". Journal of Clinical Microbiology 46 (3). doi:. PMID 18199784.</cite></ref> H3N2 evolved from H2N2 by antigenic shift.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Lindstrom Stephen E, Cox Nancy J, Klimov Alexander (15 October 2004). "Genetic analysis of human H2N2 and early H3N2 influenza viruses, 1957–1972: evidence for genetic divergence and multiple reassortment events". Virology 328 (1): 101–19. doi:. PMID 15380362.</cite></ref> In August 2004, researchers in China found H5N1 in pigs.<ref name="timeline"> Template:Cite web</ref>
These H5N1 infections may be quite common: in a survey of 10 apparently healthy pigs housed near poultry farms in West Java, where avian flu had broken out, five of the pig samples contained the H5N1 virus. The Indonesian government has since found similar results in the same region. Additional tests of 150 pigs outside the area were negative.<ref>Template:Cite news</ref><ref>Template:Cite news report on pigs as carriers.</ref>
[edit] Signs and symptoms
[edit] In swine
In pigs influenza infection produces fever, lethargy, sneezing, coughing, difficulty breathing and decreased appetite.<ref name=Kothalawala><cite style="font-style:normal">Kothalawala H, Toussaint MJ, Gruys E (June 2006). "An overview of swine influenza". Vet Q 28 (2): 46–53. PMID 16841566.</cite></ref> In some cases the infection can cause abortion. Although mortality is usually low (around 1-4%),<ref name=Merck/> the virus can produce weight loss and poor growth, causing economic loss to farmers.<ref name=Kothalawala/> Infected pigs can lose up to 12 pounds of body weight over a 3 to 4 week period.<ref name=Kothalawala/>
[edit] In humans

Direct transmission of a swine flu virus from pigs to humans is occasionally possible (called zoonotic swine flu). In all, 50 cases are known to have occurred since the first report in medical literature in 1958, which have resulted in a total of six deaths.<ref name=Myers><cite style="font-style:normal">Myers KP, Olsen CW, Gray GC (April 2007). "Cases of swine influenza in humans: a review of the literature". Clin. Infect. Dis. 44 (8): 1084–8. doi:. PMID 17366454. PMC:1973337.</cite></ref> Of these six people, one was pregnant, one had leukemia, one had Hodgkin disease and two were known to be previously healthy.<ref name=Myers/> Despite these apparently low numbers of infections, the true rate of infection may be higher, since most cases only cause a very mild disease, and will probably never be reported or diagnosed.<ref name=Myers/>
thumb|In this video, Dr. Joe Bresee, with CDC's Influenza Division, describes the symptoms of swine flu and warning signs to look for that indicate the need for urgent medical attention.
See also: See this video with subtitles on YouTube [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0wK1127fHQ4&feature=channel_page]
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in humans the symptoms of the 2009 "swine flu" H1N1 virus are similar to those of influenza and of influenza-like illness in general. Symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, headache, chills and fatigue. The 2009 outbreak has shown an increased percentage of patients reporting diarrhea and vomiting.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> The 2009 H1N1 virus is not zoonotic swine flu, as it is not transmitted from pigs to humans, but from person to person.
Because these symptoms are not specific to swine flu, a differential diagnosis of probable swine flu requires not only symptoms but also a high likelihood of swine flu due to the person's recent history. For example, during the 2009 swine flu outbreak in the United States, CDC advised physicians to "consider swine influenza infection in the differential diagnosis of patients with acute febrile respiratory illness who have either been in contact with persons with confirmed swine flu, or who were in one of the five U.S. states that have reported swine flu cases or in Mexico during the 7 days preceding their illness onset."<ref name=CDCguideHD>Template:Cite web</ref> A diagnosis of confirmed swine flu requires laboratory testing of a respiratory sample (a simple nose and throat swab).<ref name=CDCguideHD/>
The most common cause of death is respiratory failure, other causes of death are pneumonia (leading to sepsis)<ref>http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/31889365/ns/health-swine_flu/</ref>, high fever (leading to neurological problems), dehydration (from excessive vomiting and diarrhea) and electrolyte imbalance. Fatalities are more likely in young children and the elderly.
[edit] Prevention
Prevention of swine influenza has three components: prevention in swine, prevention of transmission to humans, and prevention of its spread among humans.
[edit] Prevention in swine
Methods of preventing the spread of influenza among swine include facility management, herd management, and vaccination (ATCvet code: Template:ATCvet). Because much of the illness and death associated with swine flu involves secondary infection by other pathogens, control strategies that rely on vaccination may be insufficient.
Control of swine influenza by vaccination has become more difficult in recent decades, as the evolution of the virus has resulted in inconsistent responses to traditional vaccines. Standard commercial swine flu vaccines are effective in controlling the infection when the virus strains match enough to have significant cross-protection, and custom (autogenous) vaccines made from the specific viruses isolated are created and used in the more difficult cases.<ref> Template:Cite web</ref><ref>Template:Cite web</ref> Present vaccination strategies for SIV control and prevention in swine farms typically include the use of one of several bivalent SIV vaccines commercially available in the United States. Of the 97 recent H3N2 isolates examined, only 41 isolates had strong serologic cross-reactions with antiserum to three commercial SIV vaccines. Since the protective ability of influenza vaccines depends primarily on the closeness of the match between the vaccine virus and the epidemic virus, the presence of nonreactive H3N2 SIV variants suggests that current commercial vaccines might not effectively protect pigs from infection with a majority of H3N2 viruses.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Gramer Marie René, Lee Jee Hoon, Choi Young Ki, Goyal Sagar M, Joo Han Soo (July 2007). "Serologic and genetic characterization of North American H3N2 swine influenza A viruses". Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research 71 (3): 201–206. PMID 1899866.</cite></ref><ref name="pmid17366454"> <cite style="font-style:normal">Myers KP, Olsen CW, Gray GC (April 2007). "Cases of swine influenza in humans: a review of the literature". Clin Infect Dis 44 (8): 1084–8. doi:. PMID 17366454.</cite></ref> The United States Department of Agriculture researchers say that while pig vaccination keeps pigs from getting sick, it does not block infection or shedding of the virus.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
Facility management includes using disinfectants and ambient temperature to control virus in the environment. The virus is unlikely to survive outside living cells for more than two weeks, except in cold (but above freezing) conditions, and it is readily inactivated by disinfectants.<ref name=Merck/> Herd management includes not adding pigs carrying influenza to herds that have not been exposed to the virus. The virus survives in healthy carrier pigs for up to 3 months and can be recovered from them between outbreaks. Carrier pigs are usually responsible for the introduction of SIV into previously uninfected herds and countries, so new animals should be quarantined.<ref name=cfsph/> After an outbreak, as immunity in exposed pigs wanes, new outbreaks of the same strain can occur.<ref name=Merck/>
[edit] Prevention in humans
- Prevention of pig to human transmission
The transmission from swine to human is believed to occur mainly in swine farms where farmers are in close contact with live pigs. Although strains of swine influenza are usually not able to infect humans this may occasionally happen, so farmers and veterinarians are encouraged to use a face mask when dealing with infected animals. The use of vaccines on swine to prevent their infection is a major method of limiting swine to human transmission. Risk factors that may contribute to swine-to-human transmission include smoking and not wearing gloves when working with sick animals.<ref><cite style="font-style:normal">Ramirez A, Capuano AW, Wellman DA, Lesher KA, Setterquist SF, Gray GC (June 2006). "Preventing zoonotic influenza virus infection". Emerging Infect. Dis. 12 (6): 996–1000. PMID 16707061. PMC:1673213.</cite></ref>
- Prevention of human to human transmission
Influenza spreads between humans through coughing or sneezing and people touching something with the virus on it and then touching their own nose or mouth.<ref name=CDCspread> Template:Cite web</ref> Swine flu cannot be spread by pork products, since the virus is not transmitted through food.<ref name=CDCspread/> The swine flu in humans is most contagious during the first five days of the illness although some people, most commonly children, can remain contagious for up to ten days. Diagnosis can be made by sending a specimen, collected during the first five days for analysis.<ref> Template:Cite web</ref>
Recommendations to prevent spread of the virus among humans include using standard infection control against influenza. This includes frequent washing of hands with soap and water or with alcohol-based hand sanitizers, especially after being out in public.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> Chance of transmission is also reduced by disinfecting household surfaces, which can be done effectively with a diluted chlorine bleach solution.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> Although the current trivalent influenza vaccine is unlikely to provide protection against the new 2009 H1N1 strain,<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> vaccines against the new strain are being developed and could be ready as early as June 2009.<ref>Template:Cite news</ref>
Experts agree that hand-washing can help prevent viral infections, including ordinary influenza and the swine flu virus. Influenza can spread in coughs or sneezes, but an increasing body of evidence shows small droplets containing the virus can linger on tabletops, telephones and other surfaces and be transferred via the fingers to the mouth, nose or eyes. Alcohol-based gel or foam hand sanitizers work well to destroy viruses and bacteria. Anyone with flu-like symptoms such as a sudden fever, cough or muscle aches should stay away from work or public transportation and should contact a doctor for advice.
Social distancing is another tactic. It means staying away from other people who might be infected and can include avoiding large gatherings, spreading out a little at work, or perhaps staying home and lying low if an infection is spreading in a community. Public health and other responsible authorities have action plans which may request or require social distancing actions depending on the severity of the outbreak.
[edit] Treatment
[edit] In swine
As swine influenza is rarely fatal to pigs, little treatment beyond rest and supportive care is required.<ref name=cfsph>Template:Cite web</ref> Instead veterinary efforts are focused on preventing the spread of the virus throughout the farm, or to other farms.<ref name=Kothalawala/> Vaccination and animal management techniques are most important in these efforts. Antibiotics are also used to treat this disease, which although they have no effect against the influenza virus, do help prevent bacterial pneumonia and other secondary infections in influenza-weakened herds.<ref name="cfsph"/>
[edit] In humans
If a person becomes sick with swine flu, antiviral drugs can make the illness milder and make the patient feel better faster. They may also prevent serious flu complications. For treatment, antiviral drugs work best if started soon after getting sick (within 2 days of symptoms). Beside antivirals, supportive care at home or in hospital, focuses on controlling fevers, relieving pain and maintaining fluid balance, as well as identifying and treating any secondary infections or other medical problems. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends the use of Tamiflu (oseltamivir) or Relenza (zanamivir) for the treatment and/or prevention of infection with swine influenza viruses; however, the majority of people infected with the virus make a full recovery without requiring medical attention or antiviral drugs.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> The virus isolates in the 2009 outbreak have been found resistant to amantadine and rimantadine.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
In the U.S., on April 27, 2009, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued Emergency Use Authorizations to make available Relenza and Tamiflu antiviral drugs to treat the swine influenza virus in cases for which they are currently unapproved. The agency issued these EUAs to allow treatment of patients younger than the current approval allows and to allow the widespread distribution of the drugs, including by non-licensed volunteers.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
[edit] See also
Template:Commonscat Template:Wikinews
[edit] Notes
[edit] Further reading
- <cite style="font-style:normal">Alexander DJ (October 1982). "Ecological aspects of influenza A viruses in animals and their relationship to human influenza: a review". J R Soc Med 75 (10): 799–811. PMID 6752410.</cite>
- <cite style="font-style:normal">Hampson AW, Mackenzie JS (November 2006). "The influenza viruses". Med. J. Aust. 185 (10 Suppl): S39–43. PMID 17115950.</cite>
- <cite style="font-style:normal">Lipatov AS, Govorkova EA, Webby RJ, et al (September 2004). "Influenza: emergence and control". J. Virol. 78 (17): 8951–9. doi:. PMID 15308692.</cite>
- <cite style="font-style:normal">Van Reeth K (2007). "Avian and swine influenza viruses: our current understanding of the zoonotic risk". Vet. Res. 38 (2): 243–60. doi:. PMID 17257572.</cite>
- <cite style="font-style:normal">Webster RG, Bean WJ, Gorman OT, Chambers TM, Kawaoka Y (March 1992). "Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses". Microbiol. Rev. 56 (1): 152–79. PMID 1579108. PMC:372859.</cite>
- <cite style="font-style:normal">Winkler WG (October 1970). "Influenza in animals: its possible public health significance". J. Wildl. Dis. 6 (4): 239–42; discussion 247–8. PMID 16512120.</cite>
[edit] External links
- UK National Pandemic Flu Service
- Official UK government information on swine flu from Directgov
- Official swine flu advice and latest information from the UK National Health Service
- Tri-Air Developments Air purification system for protection against H1N1: tested UK HPA Centre for Emergency Preparedness and Response, Porton Down, Sep 24, 2007
- 8 minute video answering common questions about the subject on fora.tv
- Swine flu charts and maps Numeric analysis and approximation of current active cases
- Worried about swine flu? Then you should be terrified about the regular flu.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - Swine Flu
- Pandemic Flu US Government Site
- World Health Organization (WHO): Swine influenza
- Medical Encyclopedia Medline Plus: Swine Flu
- Swine Flu Tracker