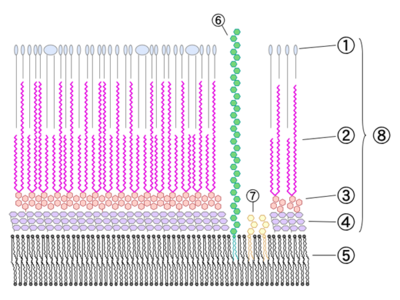
Mtb cell wall
From DrugPedia: A Wikipedia for Drug discovery
The cell wall consists of several layers (from outer, see picture right):
Contents |
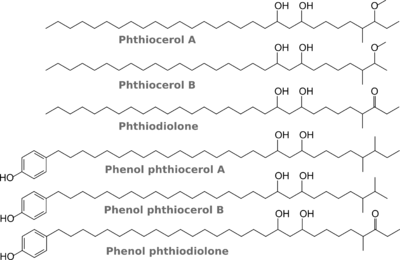
1. Phthiocerol Dimycocerosates (DIM)
DIM are esters of phthio compounds (see picture left) -- which are diols -- with methyl-branched fatty acids. The phenylphthio compounds can be glycosylated too. In all other species that have similar compounds, the chain length is shorter, except in M. bovis.
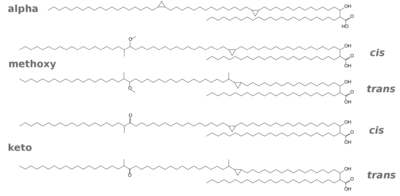
2. Mycolic acids
Mycolic acids are the longest fatty acids known from nature. They feature also cyclopropane residues in the chain which is unusual. Shown below are the five types of mycolic acids found in Mtb. The mycolic acids are bound as esters to arabinogalactan.
3. Arabinogalactan
4. Peptidoglycan
5. Plasma membrane (?)
6. Lipoarabinomannan
7. Phosphatidylinositol Mannoside
References
- Daffée M and Lanéelle MA (July 1988). "Distribution of phthiocerol diester, phenolic mycosides and related compounds in mycobacteria". J Gen Microbiol. 134 (7): 2049-55. PMID 3149973
- Glickman MS, Cahill SM, Jacobs WR (January 2001). "The Mycobacterium tuberculosis cmaA2 gene encodes a mycolic acid trans-cyclopropane synthetase". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (3): 2228–33. DOI:10.1074/jbc.C000652200. PMID 11092877.