17-Hydroxypregnenolone
From DrugPedia: A Wikipedia for Drug discovery
m |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<table align='right' border=1> | <table align='right' border=1> | ||
<tr><td> | <tr><td> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 9: | ||
</jmol> | </jmol> | ||
</td></tr></table> | </td></tr></table> | ||
| + | {{drugbox | | ||
| + | | IUPAC_name = 1-[(3S,8R,9S,10R,13S,17R)-3,17-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]ethanone | ||
| + | | CAS_number = 387-79-1 | ||
| + | | ATC_prefix = | ||
| + | | ATC_suffix = | ||
| + | | PubChem = 440573 | ||
| + | | DrugBank = | ||
| + | | molecular formula= C<sub>2</sub><sub>1</sub>H<sub>3</sub><sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | | molecular_weight = 332.48 g/mol | ||
| + | |smile= CC(=O)C1(CCC2C1(CCC3C2CC=C4C3(CCC(C4)O)C)C)O | ||
| + | | bioavailability = | ||
| + | | protein_bound = | ||
| + | | metabolism = [[Adrenal]][[Gonad]]s | ||
| + | | elimination_half-life = | ||
| + | | excretion = | ||
| + | | pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | ||
| + | | pregnancy_US = <!-- A / B / C / D / X --> | ||
| + | | pregnancy_category = | ||
| + | | legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S3 / S4 / S8 --> | ||
| + | | legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD --> | ||
| + | | legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only --> | ||
| + | | legal_status = | ||
| + | | routes_of_administration = | ||
| + | | melting_point = 268 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | [http://172.141.127.22/raghava/hmrbase/test_extract.php?db=arun&table=nphormonet&id=1006&show=SHOW-3D Show 3-D Structure] | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| - | + | '''17-Hydroxypregnenolone''' (also '''17-OH-pregnenolone''' and '''17α-hydroxypregnenolone'''), is a C21 [[steroid]] that is obtained by [[hydroxylation]] of [[pregnenolone]] at the C17α position. This step is performed by the [[mitochondria]]l [[cytochrome P450 oxidase|cytochrome P450 enzyme]] 17α-hydroxylase ([[CYP17A1]]) that is present in the [[adrenal]] and [[gonad]]s. Peak levels are reached in humans at the end of [[puberty]] and then decline.<ref>Hill M, Lukac D, Lapcik O, Sulcova J, Hampl R, Pouzar V, Starka L. Age relationships and sex differences in serum levels of pregnenolone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone in healthy subjects. Clin Chem Lab Med. 1999 Apr;37(4):439-47. PMID 10369116</ref> High levels are also achieved during [[pregnancy]]. | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
==General Properties== | ==General Properties== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 60: | ||
CC(=O)[C@]1(CCC2[C@@]1(CC[C@H]3[C@H]2CC=C4[C@@]3(CC[C@@H](C4)O)C)C)O | CC(=O)[C@]1(CCC2[C@@]1(CC[C@H]3[C@H]2CC=C4[C@@]3(CC[C@@H](C4)O)C)C)O | ||
| + | ==Prohormone== | ||
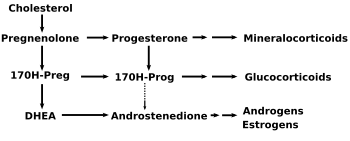
| + | [[Image:DHEA1.png|thumb|right|350px|17 OH–pregnenolone is converted from pregnenolone and gives rise to DHEA (below) and to 17 OH-progesterone (to its right)]] | ||
| + | 17-OH-pregnenolone is considered a [[prohormone]] in the formation of [[dehydroepiandrosterone]] (DHEA), itself a prohomone of the [[sex steroid]]s. | ||
| + | This conversion is mediated by the enzyme 17,20 lyase . As such 17-OH-pregenolone represents an intermediary in the delta-5-pathway that leads from pregnenolone to DHEA. 17-hydroxypregneolone is also converted to [[17-hydroxyprogesterone]], a prohomone for [[glucocorticosteroid]]s and [[androstenedione]] through the activity of 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. | ||
| - | == | + | ==Neurohormone== |
| + | There is some evidence that 17-OH-pregnenolone may have activity as a [[neurohormone]].<ref>Matsunaga M, Ukena K, [[Étienne-Émile_Baulieu|Baulieu EE]], Tsutsui K | ||
| + | 7alpha-Hydroxypregnenolone acts as a neuronal activator to stimulate locomotor activity of breeding newts by means of the dopaminergic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004 Dec 7;101(49):17282-7. PMID 15569930</ref> | ||
| - | < | + | ==Clinical use== |
| + | Measurements of 17-OH-pregnenolone are useful in the diagnosis of certain forms of [[congenital adrenal hyperplasia]].<ref>Riepe FG, Mahler P, Sippell, Partsch CJ. Longitudinal Study of Plasma Pregnenolone and 17-Hydroxypregnenolone in Full-Term and Preterm Neonates at Birth and during the Early Neonatal Period. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (2002) 87: 4301-4306 | ||
| + | [http://jcem.endojournals.org/cgi/content/full/87/9/4301]</ref> | ||
| + | In patients with [[congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency]] 17-OH-pregnenolone is increased, while in patients with [[congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency]] levels are low to absent. | ||
| + | IDS | ||
| - | + | =External Links== | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
*[http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=440573]Pubchem | *[http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=440573]Pubchem | ||
*[http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?compound+C05138]]KEGG Compound | *[http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?compound+C05138]]KEGG Compound | ||
*[http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB00363]Human Metabolome DataBase | *[http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB00363]Human Metabolome DataBase | ||
| - | + | ==References== | |
| - | [[ | + | {{reflist}} |
| + | {{Steroid metabolism intermediates}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Steroids|Hydroxypregnenolone, 17-]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Hormones]] | ||
Current revision
|
|
| 17-Hydroxypregnenolone
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 1-[(3S,8R,9S,10R,13S,17R)-3,17-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]ethanone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | 332.48 g/mol |
| Physical data | |
| Melt. point | 268 °C |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | AdrenalGonads |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Contents |
[edit] Description
17-Hydroxypregnenolone (also 17-OH-pregnenolone and 17α-hydroxypregnenolone), is a C21 steroid that is obtained by hydroxylation of pregnenolone at the C17α position. This step is performed by the mitochondrial cytochrome P450 enzyme 17α-hydroxylase (CYP17A1) that is present in the adrenal and gonads. Peak levels are reached in humans at the end of puberty and then decline.<ref>Hill M, Lukac D, Lapcik O, Sulcova J, Hampl R, Pouzar V, Starka L. Age relationships and sex differences in serum levels of pregnenolone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone in healthy subjects. Clin Chem Lab Med. 1999 Apr;37(4):439-47. PMID 10369116</ref> High levels are also achieved during pregnancy.
[edit] General Properties
*Molecular Weight
332.48
*Molecular Formula
C21H32O3
*IUPAC NAME
1-[(3S,8R,9S,10R,13S,17R)-3,17-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]ethanone
*Canonical Smiles
CC(=O)C1(CCC2C1(CCC3C2CC=C4C3(CCC(C4)O)C)C)O
*Isomeric Smiles
CC(=O)[C@]1(CCC2[C@@]1(CC[C@H]3[C@H]2CC=C4[C@@]3(CC[C@@H](C4)O)C)C)O
[edit] Prohormone
17-OH-pregnenolone is considered a prohormone in the formation of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), itself a prohomone of the sex steroids.
This conversion is mediated by the enzyme 17,20 lyase . As such 17-OH-pregenolone represents an intermediary in the delta-5-pathway that leads from pregnenolone to DHEA. 17-hydroxypregneolone is also converted to 17-hydroxyprogesterone, a prohomone for glucocorticosteroids and androstenedione through the activity of 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
[edit] Neurohormone
There is some evidence that 17-OH-pregnenolone may have activity as a neurohormone.<ref>Matsunaga M, Ukena K, Baulieu EE, Tsutsui K 7alpha-Hydroxypregnenolone acts as a neuronal activator to stimulate locomotor activity of breeding newts by means of the dopaminergic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004 Dec 7;101(49):17282-7. PMID 15569930</ref>
[edit] Clinical use
Measurements of 17-OH-pregnenolone are useful in the diagnosis of certain forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.<ref>Riepe FG, Mahler P, Sippell, Partsch CJ. Longitudinal Study of Plasma Pregnenolone and 17-Hydroxypregnenolone in Full-Term and Preterm Neonates at Birth and during the Early Neonatal Period. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (2002) 87: 4301-4306
[1]</ref>
In patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency 17-OH-pregnenolone is increased, while in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency levels are low to absent. IDS